A myocardial infarction, commonly referred to as a heart attack, is a critical medical condition wherein the blood flow to a specific section of the heart muscle is obstructed, typically caused by the presence of a blood clot. This disruption in the supply of blood can result in harm or fatality of the affected heart tissue. It is imperative to comprehend the factors, indications, and preventive measures linked to heart attacks in order to effectively prevent and handle this severe cardiac incident.
Causes of Heart Attacks:
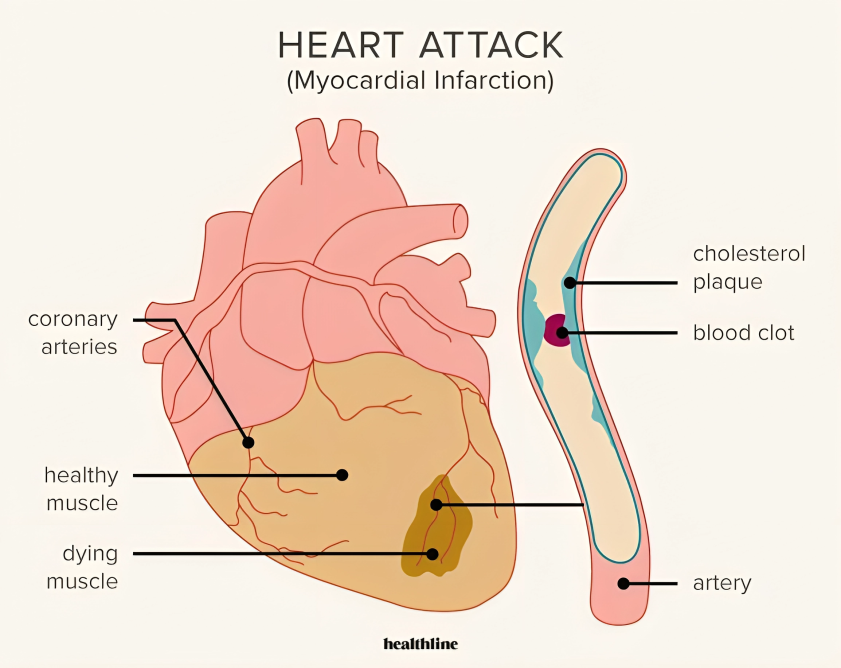
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the primary cause of heart attacks. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients, become narrowed or blocked due to the accumulation of cholesterol, fat, and other substances on the artery walls, known as plaque.
- Blood clots can also obstruct an artery, disrupting blood flow to the heart. These clots often form in arteries that are already narrowed by plaque.
- In some cases, the coronary arteries may experience spasms, causing them to constrict and temporarily reduce or block blood flow to the heart muscle. This spasm can result in a heart attack.
- Atherosclerosis, the gradual buildup of plaque in the arteries, contributes to the narrowing and hardening of the arteries, thereby increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Symptoms of Heart Attacks:
It is of utmost importance to promptly seek medical attention by recognizing the signs of a heart attack. Typical symptoms encompass:
- Chest Discomfort: Unpleasant pressure, tightness, fullness, or pain in the center or left side of the chest that could be intermittent or last for a brief period.
- Upper Body Discomfort: Pain or discomfort that may spread to the arms (typically the left arm), back, neck, jaw, or abdomen.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing or feeling short of breath, often coupled with chest discomfort.
- Cold Sweats: Excessive sweating, clammy skin, and a sense of impending danger.
- Nausea and Dizziness: Sensation of nausea, dizziness, or light-headedness, which might be accompanied by vomiting.
Precautions and Risk Factors:
- Making Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Embracing a heart-healthy way of life significantly diminishes the likelihood of experiencing heart attacks. This encompasses maintaining a well-balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and refraining from tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Consistent check-ups with healthcare professionals aid in monitoring and managing risk factors like high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
- Medication Adherence: It is crucial to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen for conditions such as hypertension or high cholesterol in order to effectively manage these risk factors.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to the development of heart disease. Adopting stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises can prove to be advantageous.
- Awareness of Family History: Being knowledgeable about one’s family history of heart disease enables individuals and healthcare providers to assess overall risk and implement preventive measures.
It is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures related to heart attacks in order to enhance heart health and avoid this serious condition. Through embracing a lifestyle that promotes heart health, being alert for symptoms, and managing risk factors, people can actively protect their cardiovascular health. Timely identification and immediate medical attention are vital in reducing the consequences of a heart attack and enhancing the likelihood of a full recovery.